JSON是前后端交互的重要数据类型之一,使用Gin Web框架可以很方便地将HTTP请求报文中JSON格式的Body数据解析到结构体Struct或字典Map数据结构中。
环境
go version go1.14.3 windows/amd64
github.com/gin-gonic/gin v1.6.3
1. 结论
参考 Fix #216: Enable to call binding multiple times in some formats #1341

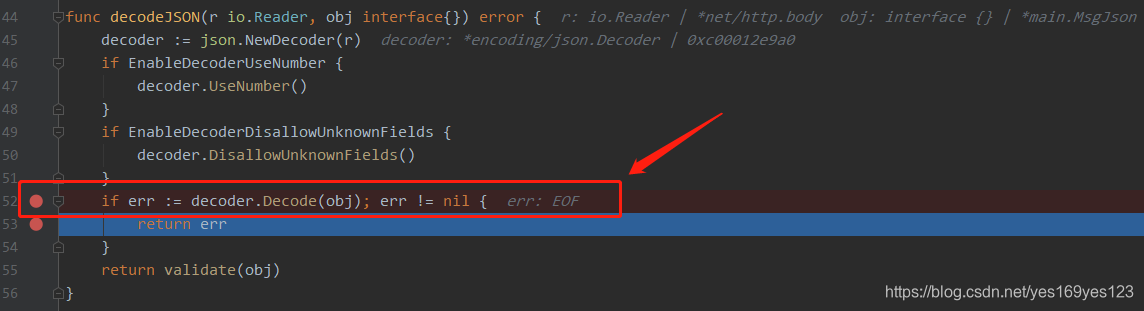
ShouldBindJSON方法是最常用解析JSON数据的方法之一,但在重复调用的情况下会出现EOF的报错,这个原因出在ShouldBindJSON在调用过一次之后context.request.body.sawEOF的值是false导致,所以如果要多次绑定多个变量,需要使用ShouldBindBodyWith。
至于为什么单次绑定不优选使用BindJSON方法,主要因为BindJSON方法会强制抛出错误,影响正常流程。
以下为范例:
// 以下是用于存储JSON数据的结构体
type MsgJson struct {
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
// 单次绑定使用 ShouldBindJSON 方法
func bindExample(c *gin.Context) {
// ---> 声明结构体变量
var a MsgJson
// ---> 绑定数据
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&a); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(
http.StatusInternalServerError,
gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// --> 返回
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"msg": "ok"})
return
}
// 多次绑定优先使用 ShouldBindBodyWith 方法
func bindWithRightWay(c *gin.Context) {
// ---> 声明两个结构体变量用于存储JSON数据
var a, b MsgJson
// ---> 第一次解析(注意第二个参数是 binding.JSON)
if err := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&a, binding.JSON); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(
http.StatusInternalServerError,
gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// ---> 第二次解析
if err := c.ShouldBindBodyWith(&b, binding.JSON); err != nil {
c.AbortWithStatusJSON(
http.StatusInternalServerError,
gin.H{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
// ---> 返回
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{"msg": "ok"})
return
}
2. EOF错误复现
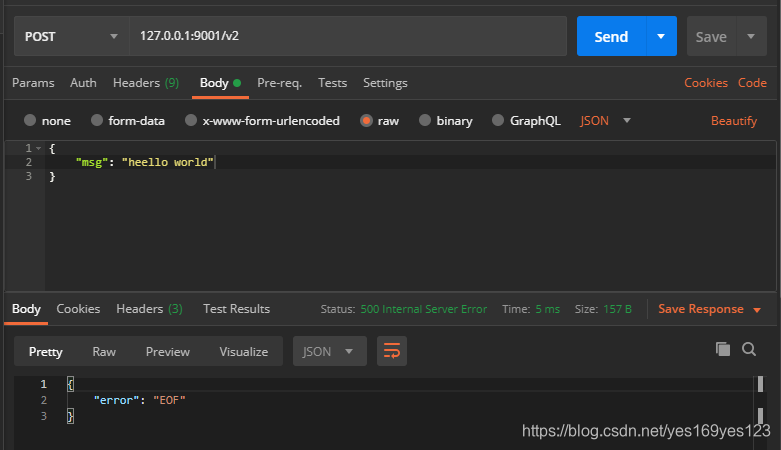
EOF错误出现在第二次使用ShouldBindJSON方法,在多次绑定的情况下,优先使用ShouldBindBodyWith,以下为❌错误示范:
type MsgJson struct {
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/v2", bindWithError)
_ = r.Run("127.0.0.1:9001")
}
func bindWithError(c *gin.Context) {
var a, b MsgJson
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&a); err != nil {....}
// ---> 注意,这里会出现EOF报错
if err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&b); err != nil {....}
.......
return
}
Postman测试结果:
Goland断点调试:
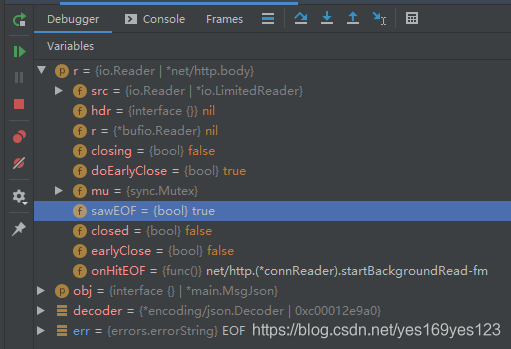
3. ShouldBindBodyWith 源码分析
ShouldBindBodyWith和ShouldBindWith很像,但它保存了requests的Body到上下文,允许Body被继续调用。
注意:这个方法会先读取Body然后绑定,如果只绑定一次,建议使用ShouldBindWith来获得更好的性能(因为后者会直接读取并写到指定变量,而没有写入上下文)。
func (c *Context) ShouldBindBodyWith(obj interface{}, bb binding.BindingBody) (err error) {
var body []byte
// ---> 先看上下文是否已经有Body的Bytes数据
if cb, ok := c.Get(BodyBytesKey); ok {
if cbb, ok := cb.([]byte); ok {
body = cbb
}
}
// ---> 如果Body不为空的情况下,读取Body数据并写入上下文
if body == nil {
body, err = ioutil.ReadAll(c.Request.Body)
if err != nil {
return err
}
c.Set(BodyBytesKey, body)
}
return bb.BindBody(body, obj)
}
流程图

有疑问加站长微信联系(非本文作者)







