我们在网上做的工作,大部分其实就是事件,webhooks 已经成为了连接系统的主要方式,不管是用户创建、支付成功、DockerHub 镜像推送或者 Git 仓库上的合并请求,这些都是非常有用并且轻量级的共享信息的方式
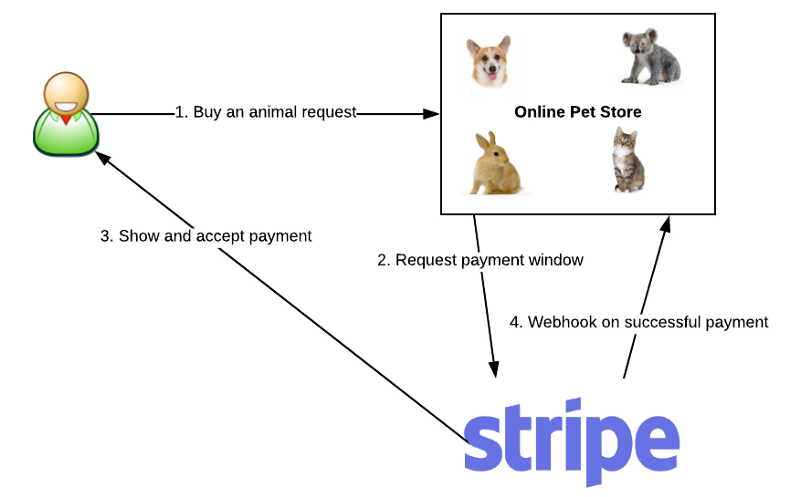
那么,webhook 究竟是什么呢?webhook 是应用给其它应用提供实时信息的一种方式。信息一产生,webhook 就会把它发送给已经注册的应用,这就意味着你能实时得到数据。不像传统的 APIs 方式,你需要用轮询的方式来获得尽可能实时的数据。这一点使得 webhook 不管是在发送端还是接收端都非常高效。由于大部分服务提供商对 API 的访问有一定限制,所以要么采用 webhook 方式,要么采用传统的轮询方式,不过这样客户端数据会有一些(或者比较多的)滞后。上面的图是用户发起的一个典型的支付流程的示例。
Webhook 有时被叫做「反向 APIs」,因为它返回的信息和正常 API 返回的差不多,并且你还得设计一个 webhook 可以使用的 API。webhook 会向你的应用发送一个 HTTP 请求(通常使用 POST 方式),然后你的应用负责解析这个请求。你可以把它当成一个客户端发来的常规 API 请求,不过这时候它是一个你依赖的一个第三方的服务。
现在许多开发者都在使用比较流行的服务(比如 Strip、GitHub)提供的 webhook,你可能也想让用户接收你的应用产生的 webhook。这篇文章里,我们就是要创建这样一个简单的应用,让其它用户可以注册并且接收这个应用产生的事件。
创建一个 webhhook 分发应用
我们的这个应用将使用 Go 语言编写(这里 有 Go 语言的安装指南),但是你可以选择任何其它的语言来实现这个应用,这只是一个展示 webhook 功能的简单的例子。代码非常简单,即使你对 Go 不熟悉也很容易读懂。
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"sync"
"time"
)
// port - default port to start application on
const port = ":8090"
type WebhookRequest struct {
Name string
Destination string
}
func main() {
dispatcher := &Dispatcher{
client: &http.Client{},
destinations: make(map[string]string),
mu: &sync.Mutex{},
}
// preparing HTTP server
srv := &http.Server{Addr: port, Handler: http.DefaultServeMux}
// webhook registration handler
http.HandleFunc("/webhooks", func(resp http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
dec := json.NewDecoder(req.Body)
var wr WebhookRequest
err := dec.Decode(&wr)
if err != nil {
resp.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
dispatcher.add(wr.Name, wr.Destination)
})
// start dispatching webhooks
go dispatcher.Start()
fmt.Printf("Create webhooks on http://localhost%s/webhooks \n", port)
// starting server
err := srv.ListenAndServe()
if err != http.ErrServerClosed {
log.Fatalf("listen: %s\n", err)
}
}
type Dispatcher struct {
client *http.Client
destinations map[string]string
mu *sync.Mutex
}
func (d *Dispatcher) Start() {
ticker := time.NewTicker(5 * time.Second)
defer ticker.Stop()
for {
select {
case <-ticker.C:
d.dispatch()
}
}
}
func (d *Dispatcher) add(name, destination string) {
d.mu.Lock()
d.destinations[name] = destination
d.mu.Unlock()
}
func (d *Dispatcher) dispatch() {
d.mu.Lock()
defer d.mu.Unlock()
for user, destination := range d.destinations {
go func(user, destination string) {
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", destination, bytes.NewBufferString(fmt.Sprintf("Hello %s, current time is %s", user, time.Now().String())))
if err != nil {
// probably don't allow creating invalid destinations
return
}
resp, err := d.client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
// should probably check response status code and retry if it's timeout or 500
return
}
fmt.Printf("Webhook to '%s' dispatched, response code: %d \n", destination, resp.StatusCode)
}(user, destination)
}
}
运行这个webhook 应用
要使用这个 webhook 应用,我们需要一个可以接收 webhook 消息并且调试的一个终端。为了完成这个任务,我们选择了 https://bin.webhookrelay.com/ 这个免费的服务。打开这个链接后,会被重定向到一个唯一的地址,那个就是我们要使用的终端地址,后面我们很快就会用到这个地址。
接下来让我们启动这个应用:
$ go run main.go
Create webhooks on http://localhost:8090/webhooks
现在把刚才生成的终端地址注册到我们的应用里:
curl --request POST \
--url http://localhost:8090/webhooks \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{
"name": "joe",
"destination": "https://bin.webhookrelay.com/v1/webhooks/821024d7-12a0-4b41-99f2-71fcc2906989"
}'
注册完以后,我们应该很快看到日志信息:
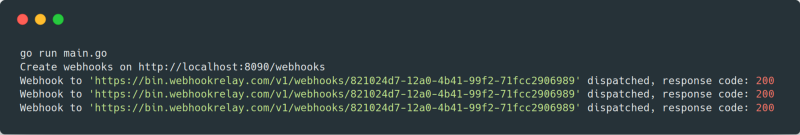
在网页终端里应该会看到应用发来的请求:
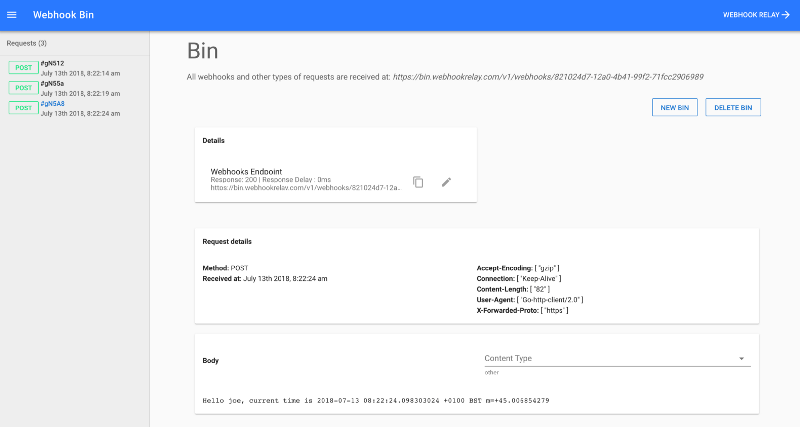
总结
总的说,webhook 和普通的 API 请求是一样的,都是事件,都是为了在系统间共享信息。API 轮询在之前可能是一个比较好的解决方案,但是如果有过多的用户采用这种方式,可能给服务器带来很大的负担甚至导致当机。
要成功实现一个 webhook 需要考虑以下几点:
- 用户应该可以指定 webhook 的地址
- 大多数系统只允许连接到一个 webhook, 你可能需要允许链接到多个
- 如果请求的返回码大于 500, 则重新请求。可能有人认为当请求返回的是 4 开头的值时,才应该重新请求,因为这说明刚才的请求是无效的
如果对 webhook 感兴趣,可以看一下我们写的一些 例子,从这些例子里你可以学会如何接收本地或者局域网 webhook 发送的信息。总之 webhook 非常灵活。
2018 年 7 月 13 号发表于 webhookrelay.com
via: https://itnext.io/what-is-a-webhook-and-how-to-create-one-f7057d2cc0a
作者:Karolis Rusenas 译者:jettyhan 校对:polaris1119
本文由 GCTT 原创翻译,Go语言中文网 首发。也想加入译者行列,为开源做一些自己的贡献么?欢迎加入 GCTT!
翻译工作和译文发表仅用于学习和交流目的,翻译工作遵照 CC-BY-NC-SA 协议规定,如果我们的工作有侵犯到您的权益,请及时联系我们。
欢迎遵照 CC-BY-NC-SA 协议规定 转载,敬请在正文中标注并保留原文/译文链接和作者/译者等信息。
文章仅代表作者的知识和看法,如有不同观点,请楼下排队吐槽
有疑问加站长微信联系(非本文作者))









