具有监控存活的 goroutine 数量功能的 APM (Application Performance Monitoring) 应用程序性能监控可以轻松查出 goroutine 泄漏。例如 NewRelic APM 中 goroutine 的监控。
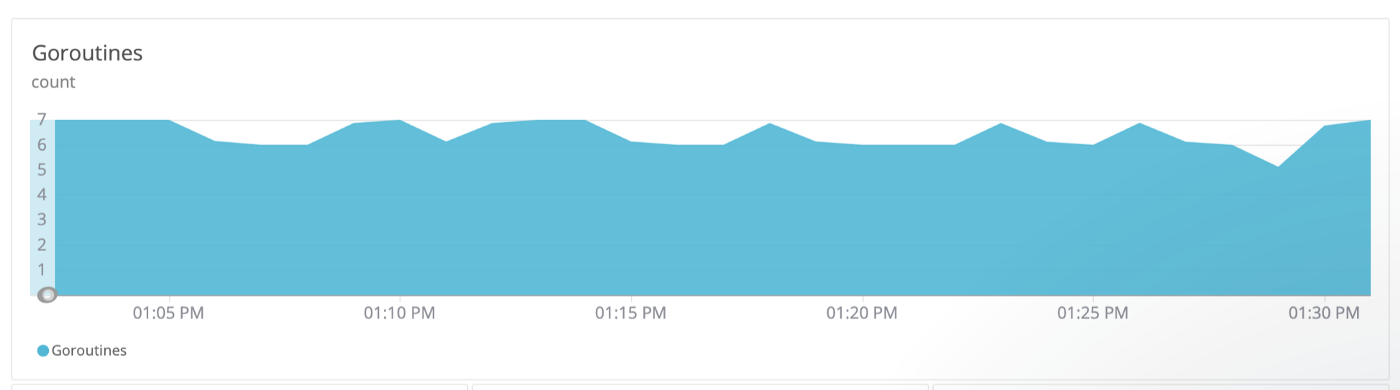
goroutine 泄漏会导致内存中存活的 goroutine 数量不断上升,直到服务宕机为止。因此,可以在代码部署之前,通过一些方法来检查程序中是否存在泄漏
泄漏检测
隶属于 Uber 公司的 Go 团队在 GitHub 开源了他们的goroutine 泄漏检测器 出来,一个与单元测试结合使用的工具。 goleak 可以监控当前测试代码中泄漏的 goroutine。下面有一个 goroutine 泄漏的例子:
func leak() error {
go func() {
time.Sleep(time.Minute)
}()
return nil
}
测试代码:
func TestLeakFunction(t *testing.T) {
defer goleak.VerifyNone(t)
if err := leak(); err != nil {
t.Fatal("error not expected")
}
}
运行结果中展示了 goroutine 的泄漏情况:

从报错信息中我们可以提取出两个有用的信息:
- 报错信息顶部为泄漏的 goroutine 的堆栈信息,以及 goroutine 的状态,可以帮我们快速调试并了解泄漏的 goroutine
- 之后为 goroutineID,在使用 trace 可视化的时候很有用,以下是通过
go test -trace trace.out生成的用例截图:
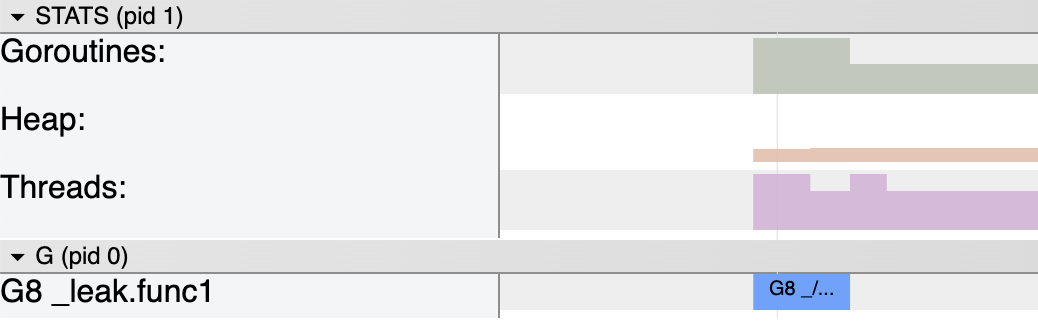
之后,我们就可以从这些 trace 中获取到 goroutine 的详细执行情况。
到此,我们已经检测到了泄漏的 goroutine,并且知道了它详细的运行情况。现在,我们需要通过学习这个库的运行原理来了解这种检测方法的局限性。
运行原理
启用泄漏检测的唯一要求就是在测试代码结束之前,调用 goleak 库来检测泄漏的 goroutine。事实上,goleak 检测了所有的 goroutine 而不是只检测泄漏的 goroutine
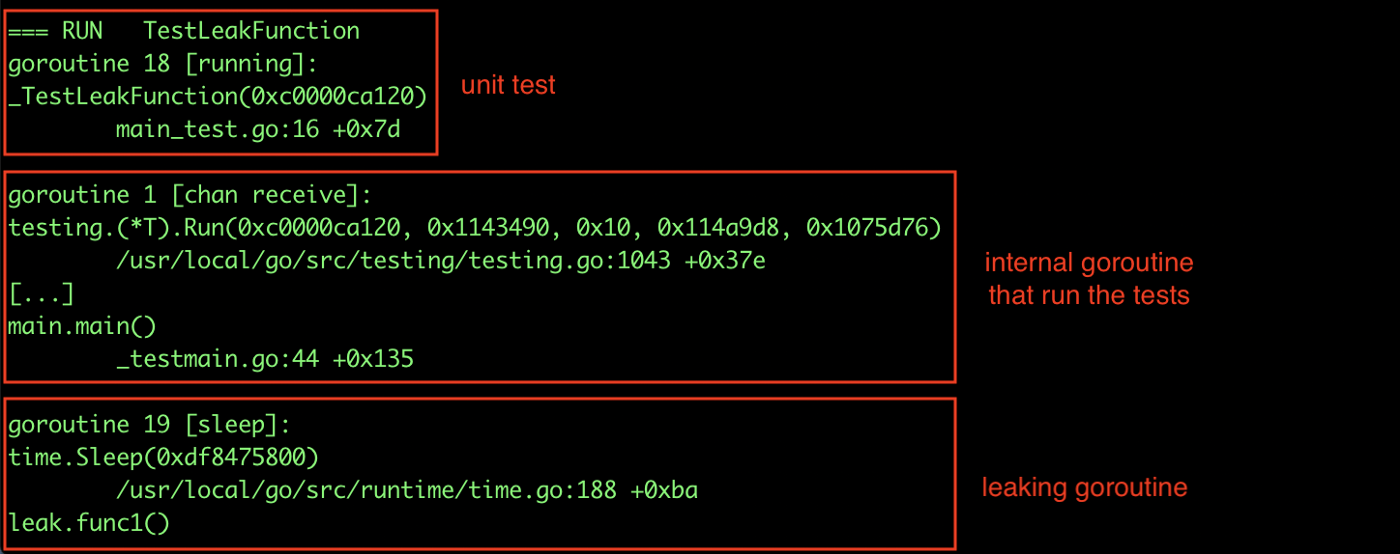
goleak 运行结果中首先列出了所有存在的 goroutine,以下是运行结果的完成截图:
goroutine 的堆栈信息由 golang 标准库中的
runtime.Stack,它可以被任何人取到。不过,Goroutine 的 ID 是拿不到的
之后,goleak 解析所有的 goroutine 出并通过以下规则过滤 go 标准库中产生的 goroutine:
- 由 go test 创建来运行测试逻辑的 goroutine。例如上图中的第二个 goroutine
- 由 runtime 创建的 goroutine,例如监听信号接收的 goroutine。想要了解更多相关信息,请参阅Go: gsignal, Master of goroutine
- 当前运行的 goroutine,例如上图的第一个 goroutine
经过此次过滤后,如果没有剩余的 goroutine,则表示没有发生泄漏。但是 goleak 还是存在一下缺陷:
- 三方库或者运行在后台中,遗漏的 goroutine 将会造成虚假的结果(无 goroutine 泄漏)
- 如果在其他未使用 goleak 的测试代码中使用了 goroutine,那么泄漏结果也是错误的。如果这个 goroutine 一直运行到下次使用 goleak 的代码, 则结果也会被这个 goroutine 影响,发生错误。
goleak 库虽然不是完美的,但是了解其局限性和缺陷,也可以尽量避免因为 goroutine 泄漏,而要调试在生产环境中的代码。
有意思的是,在 net/http 库中也使用了这个库来检测泄漏的 goroutine。下面是一些测试代码中的使用 demo:

上图中的 afterTest 中可以添加 goleak 的调用逻辑以查看 goroutine 的信息,以发现可能会出现泄漏的 goroutine。
via: https://medium.com/a-journey-with-go/go-goroutine-leak-detector-61a949beb88
作者:Vincent Blanchon 译者:CengSin 校对:unknwon
本文由 GCTT 原创翻译,Go语言中文网 首发。也想加入译者行列,为开源做一些自己的贡献么?欢迎加入 GCTT!
翻译工作和译文发表仅用于学习和交流目的,翻译工作遵照 CC-BY-NC-SA 协议规定,如果我们的工作有侵犯到您的权益,请及时联系我们。
欢迎遵照 CC-BY-NC-SA 协议规定 转载,敬请在正文中标注并保留原文/译文链接和作者/译者等信息。
文章仅代表作者的知识和看法,如有不同观点,请楼下排队吐槽
有疑问加站长微信联系(非本文作者))








