1、什么是接口?
在面向对象的语言中,接口是用来限制实现类行为的。怎么理解这句话呢?
定义一个Person接口,我只会站在我的角度上考虑问题,比如Person(人),自然想到会吃饭、睡觉等:
interface Person { 聽 聽 聽 // 人会吃饭 聽 聽 聽 void eat(); 聽 聽 聽 // 人会睡觉 聽 聽 聽 void sleep(); } |
我是站在接口角度上考虑接口如何定义,此时不会过多考虑实现类的行为。
这很正常,因为我不能确定谁会使用我的接口,有一天SuperMan说:“我要用你定义的接口”,那SuperMan必须用implements实现Person接口的行为:
// SuperMan实现Person接口 public class SuperMan implements Person { 聽 聽 聽 // 超人会吃饭 聽 聽 聽 聽public void eat() 聽 聽 聽 聽{ 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 System.out.println("super man can eat."); 聽 聽 聽 聽} 聽 聽 聽 聽// 超人会睡觉 聽 聽 聽 聽public void sleep() 聽 聽 聽 聽{ 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 System.out.println("super man can sleep."); 聽 聽 聽 聽} } |
等到SuperMan实现完了之后,他对我说:“作为超人,我是会飞的哦~”
这时作为Person定义者的我,只有两个选择:
对SuperMan说:“飞是你自己的行为,我不帮你定义这种行为!”。可是经过若干万年之后人类进化了怎么办?
对SuperMan说:“好吧,我帮你定义这种行为,可是一旦Person有了fly,你也必须实现fly”
其实无论上面哪种结果,都相当于接口把实现类绑架了。
【备注】:悄悄地告诉你,上面的代码是Java语言 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽
2、GO语言的接口呢?
GO语言有接口类型(interface{}),它与面向对象的接口含义不同,GO语言的接口类型与数组(array)、切片(slice)、集合(map)、结构体(struct)是同等地位的。怎么理解这句话呢?
我们前面已知道:
| var num int 聽// 定义了一个int型变量num |
同理:
| var any interface{} // 定义了一个接口类型变量any |
从这个角度上看,GO的interface{}与面向对象的接口是不一样吧。 聽聽更加不一样的是,interface{}是一个任意类型,或者说是万能类型。
聽聽更加不一样的是,interface{}是一个任意类型,或者说是万能类型。
3、GO语言的任意类型
也就是说定义一个变量为interface{}类型,可以把任意的值赋给这个变量,例如:
var v1 interface{} = 250 聽 聽 聽 // 把int值赋给interface{} var v2 interface{} = "eagle" // 把string值赋给interface{} var v3 interface{} = &v1 聽 聽 聽// 把v1的地址赋给interface{} |
当然函数的入参类型也可以是interface{},这样函数就可以接受任意类型的参数,例如GO语言标准库fmt中的函数Println()
func Println(args ...interface{}){ 聽 聽 聽 聽 // 略 } |
任意类型看起来很爽,可以把任意的值都赋给interface{}类型变量,就像JDK1.4时的Vector,那时候Java还没有泛型的概念,任意值都可以向Vector里面放,但问题也接踵而至:
// 定义一个长度为3的Any类型数组,求数组元素之和,即anyArr[0]+anyArr[1]+anyArr[2] var anyArr [3]interface{} anyArr[0] = "eagle" 聽 聽// anyArr[0]赋值为字符串 anyArr[1] = 20 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 // anyArr[1]赋值为int anyArr[2] = 75.3 聽 聽 聽 聽// anyArr[2]赋值为float64 // 此时若求和,会有什么结果呢? fmt.Println(anyArr[0] + anyArr[1] + anyArr[2]) |
4、类型判断
上例直观上来看,string不能和int直接相加,所以我们需要判断元素类型,若元素类型是数字型的,我们就执行“+”操作;若元素类型是字符串型的,我们就跳过。这里需要引入另外一个知识:switch-type
即:拿到一个interface{}之后,可以结合switch语句判断变量的类型 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽
例如:
var v interface{} = 3 switch v.(type){ 聽 聽 聽 case int: 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 fmt.Println("3 is int") 聽 聽 聽 case string: 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 fmt.Println("3 is string") 聽 聽 聽 default: 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 fmt.Println("unkown type") } |
所以上面的例子可以进一步修改如下:
// 定义一个长度为3的Any类型数组,求数组元素之和,即anyArr[0]+anyArr[1]+anyArr[2] var anyArr [3]interface{} anyArr[0] = "eagle" anyArr[1] = 20 anyArr[2] = 75.3 // 定义一个总和变量total var total float64 = 0 // 遍历Any类型数组 for i := 0; i < len(anyArr); i++ { 聽 聽 聽 聽 // 针对Any类型数组中的每个元素进行类型查询 聽 聽 聽 聽 switch vType := anyArr[i].(type) { 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 case int: 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 total += float64(vType) 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 case float64: 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 total += vType 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 default: 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 // do nothing 聽 聽 聽 聽 } } // 打印Any类型数组中数字之和 fmt.Println(total) |
5、interface类型与struct类型
聽从上面看interface类型很简单嘛,或许吧。
我们再回顾一下struct类型,struct类型是一个结构体,里面可以定义成员,它类似面向对象的一个类,类里面可以定义成员变量,比如:
// 定义一个person结构体,里面有姓名、年龄、身高、体重成员 type person struct{ 聽 聽 聽 聽 name 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 string 聽 聽 聽 聽 age 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽int 聽 聽 聽 聽 height, weight 聽 float64 } |
那么interface类型是否也可以这样定义呢?如下:
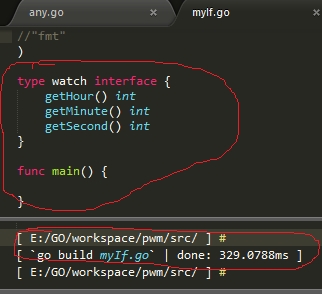
/** 聽* 定义一个手表接口,通过手表接口我们可以知道小时、分钟和秒 聽*/ type watch interface { 聽 聽 聽 聽 getHour() int 聽 聽 聽 聽 getMinute() int 聽 聽 聽 聽 getSecond() int } |
通过编译(go build myIf.go)会发现并没有抛出错误!
从结果可以看出完全可以这样定义一个类型为interface的变量watch,并且还可以为watch增加相应的方法;但与struct不同的是:struct里面的成员是变量,而interface里面的成员是函数,即我们可以使用interface定义接口。
6、interface定义接口示例
(1)GO语言接口实现
聽 聽 聽 聽周围的不少朋友现在都有一款iWatch智能手表,一般都用来运动时监控心率,这也意味着iWatch不仅能看时间这么简单。下面我们定义一个iWatch类型:
| type iWatch int 聽 聽// 定义一个iWatch类型,它实际上就是int型;相当于为int型取一个别名iWatch |
接下来为iWatch类型增加三个方法,分别为getHour()、getMinute()、getSecond()
| // 为iWatch增加getHour()方法 func (w iWatch) getHour() int { 聽 聽 聽 聽 return time.Now().Hour() } // 为iWatch增加getMinute()方法 func (w iWatch) getMinute() int { 聽 聽 聽 聽 return time.Now().Minute() } // 为iWatch增加getSecond()方法 func (w iWatch) getSecond() int { 聽 聽 聽 聽 return time.Now().Second() } |
下面是GO语言的精彩内容,请各位看客睁大眼睛:
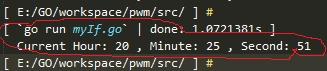
func main() { 聽 聽 聽 聽 var w watch 聽// 定义类型为watch的变量w 聽 聽 聽 聽 var t iWatch 聽// 定义类型为iWatch的变量t 聽 聽 聽 聽 w = t 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽聽// 把类型为watch的变量w赋值给类型为iWatch的变量t,这样能行的通吗? 聽 聽 聽 聽 fmt.Println("Current Hour:", w.getHour(), ", Minute:", w.getMinute(), ", Second:", w.getSecond()) } |
在这个测试代码中:
var w watch
相当于定义了一个接口变量
var t iWatch
相当于定义了一个iWatch对象
w = t
直接把对象t 赋给了接口变量w,但没有像其它面向对象语言那样,让iWatch implements watch,这样能行的通吗?
把“吗”字去掉,请看结果:
神奇吧 :)
以上是GO语言的接口实现。
(2)Java语言的接口实现
用面向对象的编程语言来解释:
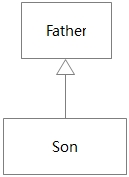
在面向对象的编程语言中,比如Son是一个实现类,Father是一个接口,Son要实现Father接口,必须使用implements显式地声明,同时在Son中实现Father里面定义的方法,比如:
interface Father{
聽 聽 聽 聽 聽getHour();
}
class Son implements Father{
聽 聽 聽 聽 聽// 实现父接口Father定义的方法getHour()
聽 聽 聽 聽 聽public int getHour(){
聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽return 20;
聽 聽 聽 聽 聽} 聽 聽 聽
}
一旦接口Father增加一个方法getSecond(),那么实现该接口的所有孩儿都必须实现getSecond()方法。在使用时:
Father father = new Son();
即孩儿对象可以赋值给Father接口
【备注】:若对上面面向对象编程语言不熟悉的话,建议看一下设计模式相关的书籍
(3)侵入式接口和非侵入式接口
像上面(2)中的Java就是侵入式接口。
GO语言中,像上面(1)所示,尽管定义了接口watch,但实现类iWatch并没有显示地声明实现该接口,只是watch中的方法都已在iWatch中实现,那么这种父子关系已建立,这种接口被称为“非侵入式接口”
7、引申
上面例子中,为iWatch定义了三个方法,现在我们修改一下这三个方法:
| // 为*iWatch增加getHour()方法 func (w *iWatch) getHour() int { 聽 聽 聽 聽 return time.Now().Hour() } // 为*iWatch增加getMinute()方法 func (w *iWatch) getMinute() int { 聽 聽 聽 聽 return time.Now().Minute() } // 为*iWatch增加getSecond()方法 func (w *iWatch) getSecond() int { 聽 聽 聽 聽 return time.Now().Second() } |
这相当于并不是为iWatch类型增加了三个方法,而是为*iWatch类型增加了三个方法,那么调用时也需要相应修改:
func main() { 聽 聽 聽 聽 var w watch 聽 聽 聽 聽 var t iWatch 聽 聽 聽 聽 w = &t 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 聽 fmt.Println("Current Hour:", w.getHour(), ", Minute:", w.getMinute(), ", Second:", w.getSecond()) } |
好了,关于GO语言的接口类型就聊到这里,请记住这么三句话:
interface是类型
interface类型的变量可以赋值
任何实现了interface类型的具体类型变量,都可以赋值给interface类型的变量
本文出自 “青客” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://qingkechina.blog.51cto.com/5552198/1675115
有疑问加站长微信联系(非本文作者)